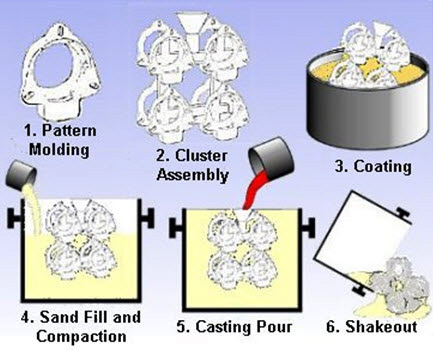
Investment casting
Water glass and silica sol investment casting are the two primary investment casting methods nowadays. The main differences are the surface roughness and cost of casting. Water glass method dewaxes into the high-temperature water, and the ceramic mold is made of water glass quartz sand. Silica sol method dewaxes into the flash fire, and silica sol zircon sand makes the ceramic mold. Silica sol method costs more but has the better surface than the water glass method.
The process can be used for both small castings of a few ounces and large castings weighing several hundred pounds. It can be more expensive than die casting or sand casting, but per-unit costs decrease with large volumes. Investment casting can produce complicated shapes that would be difficult or impossible with other casting methods. It can also produce products with exceptional surface qualities and low tolerances with minimal surface finishing or machining required.

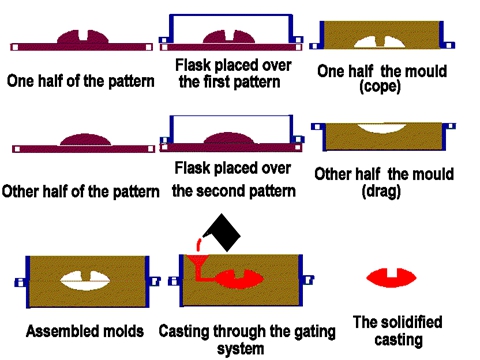
Sand casting
Sand casting, also known as sand molded casting, is a metal casting process characterized by using sand as the mold material. The term "sand casting" can also refer to an object produced via the sand casting process. Sand castings are produced in specialized factories called foundries. Over 60% of all metal castings are produced via sand casting process.
Molds made of sand are relatively cheap, and sufficiently refractory even for steel foundry use. In addition to the sand, a suitable bonding agent (usually clay) is mixed or occurs with the sand. The mixture is moistened, typically with water, but sometimes with other substances, to develop the strength and plasticity of the clay and to make the aggregate suitable for molding. The sand is typically contained in a system of frames or mold boxes known as a flask. The mold cavities and gate system are created by compacting the sand around models called patterns, by carving directly into the sand, or by 3D printing.
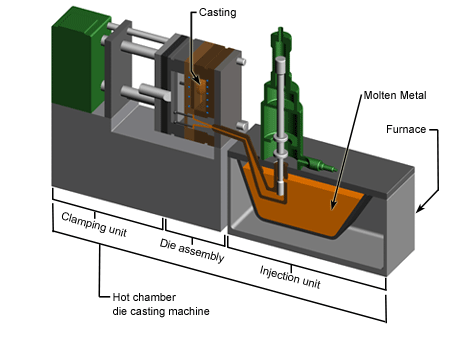
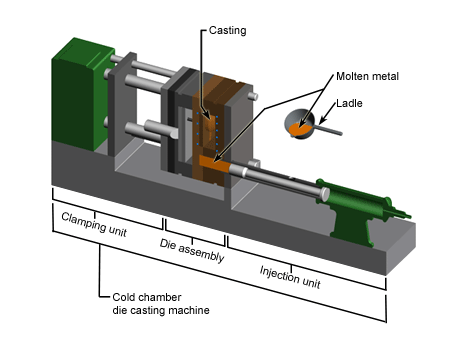
Die Casting
Die casting is a manufacturing process that can produce geometrically complex metal parts through the use of reusable molds, called dies. The die casting process involves the use of a furnace, metal, die casting machine, and die. The metal, typically a non-ferrous alloy such as aluminum or zinc, is melted in the furnace and then injected into the dies in the die casting machine. There are two main types of die casting machines - hot chamber machines (used for alloys with low melting temperatures, such as zinc) and cold chamber machines (used for alloys with high melting temperatures, such as aluminum). The differences between these machines will be detailed in the sections on equipment and tooling. However, in both machines, after the molten metal is injected into the dies, it rapidly cools and solidifies into the final part, called the casting.
Lost-foam casting
Lost-foam casting (LFC) is a type of evaporative-pattern casting process that is similar to investment casting except foam is used for the pattern instead of wax. This process takes advantage of the low boiling point of polymer foams to simplify the investment casting process by removing the need to melt the wax out of the mold.